let’s us know about Lactose intolerance

lactose intolerance
Lactose intolerance
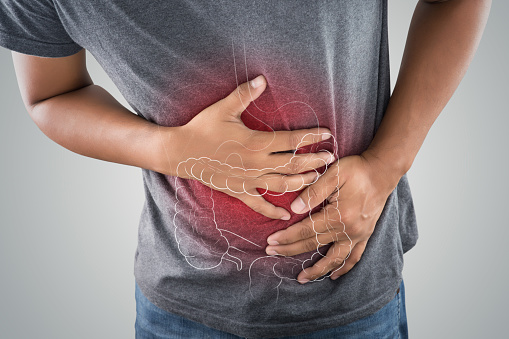
Lactose intolerance is a not unusual condition resulting from a reduced capacity to digest lactose, a sugar in dairy products. This can affect the quantity of lactose one can tolerate before symptoms develop. Symptoms can also encompass stomach pain, bloating, diarrhea, gas, and nausea.

These signs generally begin thirty mins to 2 hours after ingesting or ingesting milk-primarily based totally food. Their severity typically relies upon the quantity someone eats or drinks. Lactose intolerance no longer causes harm to the gastrointestinal tract.
Lactose intolerance is caused by the absence of the enzyme lactase inside the small intestines, interrupting lactose into glucose and galactose. There are 4 types: one, secondary, developmental, and congenital. Primary lactose intolerance occurs as the number of lactase declines as humans age. Secondary lactose intolerance is caused by harm to the small intestine.
Such harm can result from infection, celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease, or different diseases. Developmental lactose intolerance can also additionally arise in untimely infants and generally improves over a brief length of time.
Congenital lactose intolerance is an incredibly uncommon genetic ailment wherein very little lactase is crafted from birth. The onset of number one lactose intolerance, the maximum not unusual place type, is generally in past due to youth or early adulthood, however, the incidence will increase with age.
Diagnosis can be shown if signs clear up following getting rid of lactose from the diet. Other helping exams encompass hydrogen breath take a look at and stool acidity to take a look at. Other situations that could produce comparable signs encompass irritable bowel syndrome, celiac disease, and inflammatory bowel disease. Lactose intolerance isn’t like a milk allergy.
Management is generally through reducing the quantity of lactose in the diet, taking lactase supplements, or treating the underlying disease. According to Sitting with Outgrowing Big Signs, people are generally capable of drinking at least one cup of milk, with more quantities tolerated if under the influence of alcohol with a meal or during the day.
Most adults (around 65–70% of the world’s population) are stricken by lactose malabsorption. Other mammals generally lose the cap potential to digest lactose after weaning. This becomes the ancestral kingdom of all human beings earlier than the current evolution of lactase-staying power, extending lactose tolerance into adulthood.
Lactose-staying power developed independently in numerous populations, probably in addition to the domestication of dairy animals around 10,000 years ago. Today, the superiority of lactose tolerance varies broadly among areas and ethnic groups.
The cap potential to digest lactose is most common in people of European descent and, to a lesser extent, in parts of the Middle East and Africa. Traditional food cultures mirror nearby versions of intolerance, and traditionally, many societies have tailored to low stages of tolerance by making dairy merchandise that comprises much less lactose than sparkling milk.
The medicalization of lactose intolerance as a disease has been attributed to biases in study history (given that the earliest research was carried out among populations in which tolerance is the norm) and the cultural and monetary significance of milk in international locations, including the United States.
Terminology
Lactose intolerance normally refers to a syndrome characterized by one or more signs and symptoms upon consuming lactose foods. Depending on the severity of those signs and symptoms, individuals can be lactose illiberal to various degrees.

“Lactose malabsorption” refers to the physiological concomitant of lactase deficiency (i.e., the frame no longer has enough lactase to digest the quantity of lactose ingested). Hypolactasia (lactase deficiency) is an outstanding defect.
Lactose intolerance isn’t an allergy, as it isn’t an immune response, however as an alternative a sensitivity to dairy resulting from lactase deficiency. Milk allergy, happening in approximately 2% of the population, is a separate condition with wonderful signs and symptoms that arise when the presence of milk proteins causes an immune response.
signs and symptoms
The predominant manifestation of lactose intolerance is a destructive response to merchandise containing lactose (normally milk), stomach bloating, cramps, flatulence, diarrhea, nausea, borborygmi, and vomiting (mainly in adolescents). These seem one-1/2 to 2 hours after intake.

The severity of those symptoms and signs normally increases with the quantity of lactose consumed; maximum lactose-illiberal humans can tolerate a certain stage of lactose in their diets without unwell effects.
Causes
Lactose intolerance is an effect of lactase deficiency, which can be genetic (number one hypolactasia and number one congenital Anastasia) or environmentally induced (secondary or received hypolactasia).
In both cases, signs and symptoms result from inadequate lactase levels in the duodenum’s lining. Lactose, a disaccharide molecule found in milk and dairy products, can’t be absorbed immediately through the wall of the small gut into the bloodstream, so in the absence of lactase, it passes intact into the colon.
Bacteria within the colon can metabolize lactose, and the ensuing fermentation produces copious quantities of gas (a combination of hydrogen, carbon dioxide, and methane) that cause numerous stomach signs and symptoms. The unabsorbed sugars and fermentation merchandise also improve the colon’s osmotic strain, inflicting an elevated go with water drift into the bowels (diarrhea).
Lactose intolerance in toddlers (congenital lactase deficiency) results from mutations within the LCT gene. The LCT gene gives the commands for making lactase. Mutations are believed to interfere with the function of lactase, causing affected toddlers to have a critically impaired capacity to digest lactose in breast milk or formula.

Lactose intolerance in maturity results from the LCT gene’s step-by-step lowering of activity (expression) after infancy, which occurs in most people. The particular DNA series inside the MCM6 gene facilitates the manipulation of whether or not the LCT gene becomes on or off. At least a thousand years ago, a few people evolved a mutation inside the MCM6 gene that continues the LCT gene to become on even after breastfeeding is stopped. Populations that can be lactose illiberal lack this mutation.
Primary hypolactasia
Primary hypolactasia, or number one lactase deficiency, is genetic, best influences adults, and is due to the absence of a lactase endurance allele. In people without the lactase endurance allele, much less lactase is produced through the frame over time, leading to hypolactasia in adulthood. The frequency of lactase endurance, which lets in lactose tolerance, varies fairly worldwide, with the very best incidence in Northwestern Europe, declines throughout southern Europe and the Middle East, and is low in Asia and maximum in Africa, even though it is not unusual to place in pastoralist populations from Africa.
Secondary hypolactasia
Secondary hypolactasia or secondary lactase deficiency, additionally known as obtained hypolactasia or obtained lactase deficiency, is due to damage to the small intestine. This shape of lactose intolerance can arise in each baby and lactase continual adults and is normally reversible. It can be due to acute gastroenteritis, coeliac disease, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, chemotherapy, intestinal parasites (consisting of giardia), or different environmental causes.
Primary congenital lactase
Primary congenital lactase, or congenital lactase deficiency, is an incredibly rare, autosomal recessive enzyme illness that forestalls lactase expression from birth. People with congenital lactase deficiency cannot digest lactose from birth, so they cannot digest breast milk.
This genetic illness is characterized by a loss of lactase (alactasia). About forty instances had been pronounced worldwide, especially confined to Finland. Before the twentieth century, infants born with congenital lactase deficiency frequently did now no longer survive; however, loss of life prices were reduced with soybean-derived toddler formulations and synthetic lactose-unfastened dairy products.
Related: When was the Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM) Coverage

















1 thought on "let’s us know about Lactose intolerance"