How to Treat Blocked Hair Follicles

Blocked Hair Follicles
Treatment for Blocked Hair Follicles
Folliculitis is the contamination and irritation of one or more hair follicles. It might also arise everywhere, including hair-blanketed pores and skin. The rash might also look like zits that come to white guidelines on the face, chest, back, arms, legs, buttocks, or head.
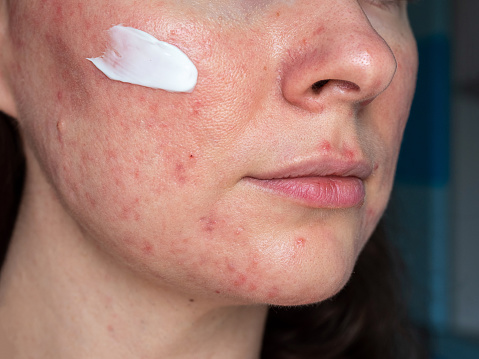
Although pimples can regularly contain superficial contamination and irritation of a few hair follicles, the circumstances of these follicles are generally no longer known as folliculitis. That period is usually reserved for separate disorder entities comprising inflamed and infected hair follicles with reasons apart from pimples.
Signs and signs and symptoms
- Histopathology of folliculitis of unknown purpose, with massive cells surrounding a hair follicle
- Rash (reddened pores and skin place)
- Itching pores and skin
- Pimples or pustules around a hair or follicle can be harassed with chookpox.
- May crust over
- Typically, they arise on the neck, armpit, or groin
- May gift as genital lesions
- Spreading from leg to arm to frame through unsuitable remedy with antibiotics
Complications
This circumstance can change into more excellent intense pores and skin circumstances, including cellulitis or abscess.
Causes
Most carbuncles boil, and different instances of folliculitis are inflamed with Staphylococcus aureus.
Folliculitis begins by creating pores and skin pathogens in a hair follicle. Hair follicles can also be broken with friction from clothing, an insect bite, blockage of the follicle, shaving, or very tight braids near the scalp. The broken follicles are then inflamed by Staphylococcus spp. Folliculitis can affect humans of all ages.[citation needed] Iron deficiency anemia is often related to persistent instances.
Bacterial

- Staphylococcus aureus folliculitis
- Hot-bath folliculitis is due to the bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Folliculitis generally occurs after sitting in a warm bath that was not wiped clean before use. Symptoms are found across the body elements in the warm bath—the legs, hips, chest, buttocks, and surrounding areas. Symptoms are amplified around regions blanketed with wet clothing, including bathing suits.
- Sycosis vulgaris, sycosis barbae, or barber’s itch is staphylococcal contamination of the hair follicles inside the bearded area of the face, generally the top lip. Shaving aggravates the circumstance.
- Gram-terrible folliculitis might also additionally seem after extended pimples are remedied with antibiotics.
Fungal
Tinea barbae is much like a barber’s itch. However, the contamination is due to the fungus T. rubrum.
Malassezia folliculitis, previously called Pityrosporum folliculitis, is due to Malassezia’s yeasts (a part of the fungus kingdom).
Mites
Demodex folliculitis is generally caused by an overgrowth of Demodex folliculorum, a mite that lives in human hair follicles. Although most humans with D. folliculorurmhave no signs or symptoms, the mite can reproduce excessively, especially in humans with oily scalps.
Viral
Herpetic folliculitis is rarer; however, it might also arise when herpes simplex virus contamination spreads to close-by hair follicles acting in corporations or clusters, generally across the mouth.
Noninfectious
Pseudofolliculitis Barbie is a disease that occurs when hair curves return to the pores and skin and causes irritation.
Eosinophilic folliculitis might also occur in individuals with impaired immune systems.
Folliculitis decalvans or tufted folliculitis generally influences the scalp. Several hairs get up from the equal hair follicle. Scarring and everlasting hair loss might also additionally follow. The purpose is unknown.
Folliculitis keloidal scarring at the nape of the neck is usually not unusual amongst men with curly hair.
Oil folliculitis is irritation of hair follicles caused by exposure to diverse oils. It usually occurs on the forearms or thighs. Refinery workers, avenue workers, mechanics, and sheep shearers are not unusual to experience it there. Even makeup might cause it.
Malignancy can also be represented by using recalcitrant instances.
Treatment
Most easy instances clear up on their own. However, first-line remedies are usually topical medications.
- A topical antiseptic remedy is ok for maximum instances.
- Topical antibiotics can be prescribed, such as mupirocin or neomycin/polymyxin B/Bacitracin ointment. Oral antibiotics can also be used.
- Some sufferers might also benefit from systemic narrow-spectrum penicillinase-resistant penicillins (including dicloxacillin in the US or flucloxacillin in the UK).
- Fungal folliculitis might also require an oral antifungal, such as fluconazole. Topical antifungals, such as econazole nitrate, can also be effective.
- Folliculitis might also recur even after signs and symptoms have long gone away.

The hair follicle is an organ determined in mammalian pores, and skin lives within the dermal layer of the pores and skin. It is made of 20 extraordinary molecular types, every with excellent functions. The hair follicle regulates hair increase through a complicated interplay among hormones, neuropeptides, and immune cells. This complex interplay induces the hair follicle to supply unique kinds of hair visible on individual body elements.
For example, terminal hairs develop at the scalp, and lanugo hairs are visible, masking the bodies of fetuses inside the uterus and in a few new child babies. The method of hair increase takes place in excellent sequential stages. The first level is known as anagen and is the energetic increase segment; telogen is the resting level; catagen is the regression of the hair follicle segment; exogen is the energetic loss of the hair segment; and ultimately, kerogen is the segment among the empty hair follicle and the increase of recent hair.
The characteristics of human hair have long been a hot topic and are still crucial in society, developmental biology, and medicine. Of all mammals, humans have the most extended increase in the segments of scalp hair compared to the increase in hair in different body elements.
For centuries, human beings have ascribed esthetics to scalp hair styling and dressing, and it’s frequently used to speak social or cultural norms in societies. In addition to defining the human look, scalp hair is protected from UV solar rays. It is an insulator in opposition to extremes of warm and bloodless temperatures. Differences within the scalp hair follicle form decide the ethnic variations in scalp hair look, period, and texture.
There are many human illnesses in which abnormalities in hair look, texture, or growth are early symptoms of a nearby ailment of the hair follicle or systemic disease. Well-recognized hair follicle diseases encompass alopecia, hair loss, hirsutism, extra hair growth, and lupus erythematosus.
Structure

- Structure of a hair follicle.
- The function and distribution of hair follicles adjust over the body. For example, the pores and skin of the arms and soles no longer have hair follicles, while the pores and skin of the scalp, forearms, legs, and genitalia have large hair follicles. Many systems make up the hair follicle. Anatomically, the hair follicle, sebaceous gland, and arrector pili muscle triad comprise the pilosebaceous unit.
A hair follicle is composed of :
- The papilla is a massive shape at the bottom of the hair follicle. The papilla is made up of connective tissue and a capillary loop. The papilla is both uncommon or non-existent inside the cell department.[contradictory]
- Around the papilla is the hair matrix.
A root sheath is composed of an outside and inner root sheath. The outside root sheath seems empty with cuboid cells while stained with H&E. The inner root sheath consists of 3 layers: Henle’s, Huxley’s, and an inner cuticle. This is non-stop with the outermost layer of the hair fiber. - The bulge is positioned within the outer root sheath on the insertion factor of the arrector pili muscle. It houses numerous kinds of stem cells, which deliver new cells to the whole hair follicle and participate in restoring the dermis after a wound. Stem cells specifically express the marker LGR5+ in vivo.
- Other systems related to the hair follicle encompass the cup wherein the follicle grows, referred to as the infundibulum, the arrector pili muscles, the sebaceous glands, and the apocrine sweat glands. Hair follicle receptors feel the placement of the hair.
Attached to the follicle is a tiny package of muscle fiber known as the arrector pili. This muscle is responsible for inflicting the follicle to become extra perpendicular to the pores and skin floor and protruding barely above the encircling pores and skin (piloerection) and a pore encased with pores and skin oil. This method affects goosebumps (or goose flesh). The sebaceous gland, which produces the oily or waxyCebuu, is also connected to the follicle. The higher the hair density, the more different sebaceous glands might be determined.
Variation
There are ethnic variations in numerous extraordinary hair characteristics. The variations in the look and texture of hair are caused by many factors: the placement of the hair bulb relative to the hair follicle, the length and form of the dermal papilla, and the curvature of the hair follicle.[1] The scalp hair follicle in Caucasians is elliptical and, therefore, produces instantly or wavy hair, while the scalp hair follicle of human beings of African descent is extra curvy, ensuing withinside the increase of tightly curled hair
Development
In utero, the epithelium and underlying mesenchyme interact to shape hair follicles.
Aging

A key factor of hair loss with age is the follicle’s aging. Follicle renewal is maintained via the stem cells related to every strand. The aging of the hair follicle seems to be primed by a sustained mobile reaction to the DNA harm that accumulates in renewing stem cells all through aging. This harm reaction entails the proteolysis of kind XVII collagen via neutrophil elastase in response to the DNA harm within the hair follicle stem cells. Proteolysis of collagen ends in removing the broken cells after terminal hair follicle miniaturization.
- Hair increase
- File: Hair-follicle biking. gov
- Hair-follicle biking
- File: Hair follicle. gov
- Hair follicle
Human hair increase
Hair grows in cycles of diverse phases: anagen is the increase section; catagen is the involuting or regressing area; and telogen is the resting or quiescent place (names derived from the use of the Greek prefixes ana-, kata-, and telos- which means up, down, and stop respectively). Each section has numerous morphologically and histologically distinguishable sub-phases. Before the beginning of biking, there is an area of follicular morphogenesis (formation of the follicle).

Likewise, there is a dropping section or exogen, independent of anagen and telogen, wherein one or numerous hairs could stand up from an available follicle exit. Usually, as much as 90% of the hair follicles are in the anagen section, while 10–14% are in telogen and 1–2% are in catagen. The cycle’s duration varies on extraordinary components of the body.
For eyebrows, the process is finished in around four months, while it takes the scalp 3–to four years to finish because hair has a far shorter duration restriction than hiding at the head. Growth cycles are managed via a chemical sign like an epidermal increase factor. DLX3 is an important regulator of hair follicle differentiation and biking
Related: How to Treat Blocked Hair Follicles














Factor certainly used!!
Amazing facts Thank you.